Fused silica glass, as a high-quality optical material, is widely used in the manufacture of optical lenses for ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared light. Its excellent transmission and optical properties make it an ideal choice for manufacturing micro-lens arrays, diffractive optical elements (DOE), lenses, and other optical components. This article will explore the transmission rate of fused silica glass and its transmission spectrum characteristics.
Transmission Rate of Fused Silica Glass
Fused silica glass displays excellent optical performance in different spectral bands. Compared to natural quartz, fused silica glass has a higher transmission rate in multiple bands. This material can provide excellent transmission performance in the ultraviolet, visible, near-infrared, and infrared bands, making it widely used in optical applications.
Specifically, the transmission rate of fused silica glass can be categorized by different bands:
JGS1 Far-Ultraviolet Optical Quartz Glass (185-2500nm)
JGS2 Ultraviolet Optical Quartz Glass (220-2500nm)
JGS3 Infrared Optical Quartz Glass (260-3500nm)
These categories indicate that fused silica glass has high transmission rates in various spectral regions, demonstrating excellent transmission performance in the far-ultraviolet band (185-2500nm) and the near-infrared band (260-3500nm). For instance, some fused silica glass models can maintain over 80% transmission in the deep ultraviolet band at 165nm, and while absorption peaks may occur around 2800nm, the transmission rate remains above 80% at 3500nm.
Transmission Spectrum of Fused Silica Glass
Fused silica glass's transmission spectrum demonstrates its optical performance in different bands. The transmission spectrum chart indicates that from 250nm to 2800nm, fused silica glass has very high transmission rates. The primary loss is due to reflection rather than absorption. The spectrum's curve exhibits the performance of fused silica glass in different bands while accounting for Fresnel reflection loss (1-R)².
Compared to natural quartz, the transmission spectrum of fused silica glass in the range of 270nm to 2600nm has lower transmission rates, especially in the ultraviolet band, where the transmission performance is significantly inferior to Fused Silica Glass. Fused silica glass offers a wider transmission range and higher transmission rates, making it a more ideal choice of optical material.
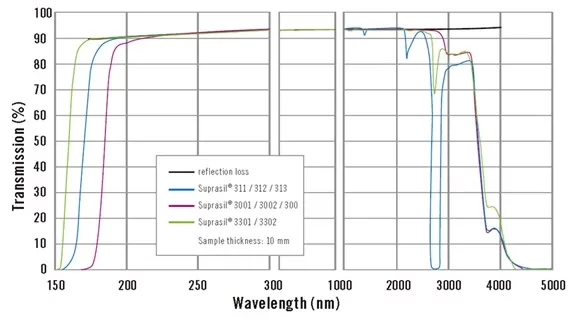
Transmission Spectrum of Synthetic Fused Silica
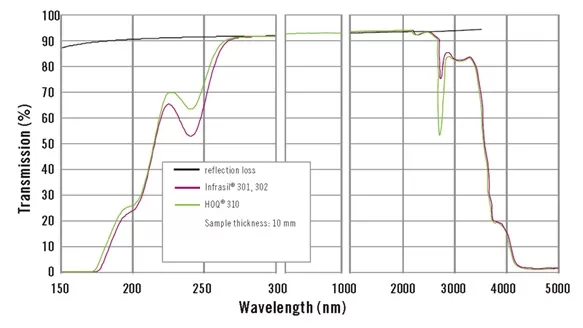
Transmission Spectrum of Natural Quartz
Applications of Quartz Crystal in the Terahertz Band
Besides its excellent performance in the ultraviolet and visible light bands, fused silica glass also has significant advantages in the terahertz band. Quartz crystals, especially Z-cut quartz crystals, exhibit over 70% transmission in the terahertz band with wavelengths greater than 50μm. This performance makes them suitable for producing terahertz lenses, quartz prisms, and terahertz windows. In the visible range and terahertz band, Z-cut quartz crystals maintain high transmission rates without altering the light's polarization state, providing significant convenience for the adjustment and application of optical systems.
Fused silica glass, with its excellent transmission rates and stable optical performance in multiple spectral bands, has become an indispensable material in modern optical systems.


















 EN
EN