The classification of optical glass lenses mainly focuses on application scenarios and optical characteristics, and their applications are highly matched with the demands of different fields for imaging quality, environmental adaptability, and spectral range.
Classification by Application Field and Core Applications
1.Consumer Electronics Field
Mobile Phone Lenses: Multi-piece glass lenses (such as 5P/6P/7P lenses) are mostly used in main camera, ultra-wide-angle, telephoto and other camera modules to meet the needs of high-definition photography and video recording. The core requirements are miniaturization and high resolution.
Camera lenses: Covering prime and zoom lenses for single-lens reflex cameras and mirrorless cameras, such as standard lenses (50mm) and telephoto lenses (200mm and above). The glass material can effectively control chromatic aberration and distortion, ensuring professional-level imaging.
2.Industrial inspection field - telecentric lenses
They are classified into object-square telecentric, image-square telecentric and bilateral telecentric types. The core advantage is that within a certain object distance range, the magnification is not affected by changes in object distance. They are widely used in dimensional measurement and defect detection (such as semiconductor chip and electronic component inspection).
Microscopic lens: Used in conjunction with a microscope, it achieves high-magnification of the microscopic world through multiple sets of high-precision glass lenses, and is applied in biomedicine (cell observation), materials science (microstructure analysis), etc.
3.Security surveillance field
Surveillance lenses: including fixed aperture fixed-focus, automatic aperture zoom and other types. Glass lenses are resistant to high and low temperatures and aging, and can work stably in harsh outdoor environments (such as high temperature, low temperature, and humidity), ensuring clear surveillance images. They are applied in road surveillance, community security, and public place surveillance.
4.Automotive electronics field
Automotive lenses: used for reversing cameras, 360° surround view, and ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems), the glass lenses need to meet the requirements of high-temperature resistance (-40℃ to 105℃), anti-vibration, and anti-glare to ensure driving safety. For instance, the front ADAS lens needs to accurately identify vehicles and pedestrians ahead through the low-distortion design of the glass lens.
5.Special spectral Field
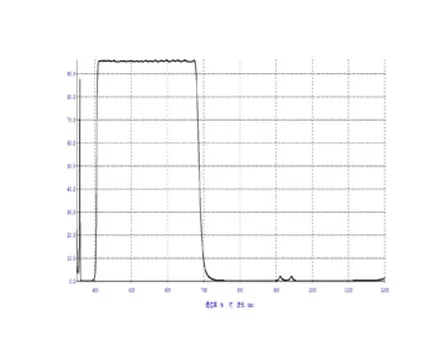
Infrared lenses: Utilizing infrared optical glass (such as sulfur-based glass, germanium glass), they can transmit through the infrared band (e.g., 8-12μm), and are applied in infrared thermal imagers, night vision devices, military reconnaissance, power inspection (for detecting equipment heating faults), and security night vision monitoring.
Ultraviolet lens: Utilizing ultraviolet optical glass, it transmits ultraviolet light and is used for UV curing, fluorescence detection (such as anti-counterfeiting of banknotes, surface defect detection of materials), and biomedicine (ultraviolet sterilization, cell analysis).
Classification by Optical Characteristics and Core Applications
1.Classification by Focal Length
Fixed Focal Length Lenses: With a fixed focal length (such as 25mm, 50mm), simple structure, and stable imaging quality, they are applied in industrial inspection (defect detection at fixed object distances), standard camera lenses, and surveillance scenarios with fixed viewing angles.
Zoom lens: The focal length is adjustable (such as 10-100mm). By moving the lens group to change the focal length, it can switch between near and far scenes for shooting. It is applied to telephoto lenses of cameras, zoom cameras for surveillance, and surround-view lenses for vehicles.
2.Classification by aberration correction ability
Achromatic lenses: They can correct chromatic aberrations of the two main colors of light (such as red and blue light), and are used in entry-level camera lenses and general industrial inspection lenses, with a relatively low cost.
Apochromatic lenses: They can correct chromatic aberration of three or more colors of light, with extremely high imaging accuracy. They are used in professional camera lenses, microscopic lenses, and high-precision measurement lenses (such as semiconductor wafer inspection).



















 EN
EN