I. Fundamental Principles
Microlens arrays (MLAs) are optical components comprising numerous miniature lenses arranged in specific patterns (e.g., hexagonal close packing or rectangular grid) on substrates. Their core functionality relies on individual lenslet's light manipulation:
Beam Splitting Principle:
Each microlens acts as an independent optical channel, dividing incident beam into sub-beams that form corresponding spot arrays at the focal plane. Key parameters include:
Focal length (f)
Aperture diameter (D)
Fill factor (>90% for high performance)
Wavefront Modulation:
Precise control of lenslet profiles (spherical/aspheric) enables phase modulation, which is fundamental for Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensors.
Light Field Sampling:
In plenoptic imaging, MLAs spatially sample angular light information to enable digital refocusing and 3D reconstruction.
II. Key Specifications
Pitch size: 10μm-1mm typical
Surface accuracy: <λ/4@632.8nm
Focal length uniformity: <±2% variation
Transmission: >95% with AR coatings
III. Major Applications
Advanced Imaging
Light field cameras (e.g., Lytro)
Confocal microscopy (sub-μm resolution)
Computational imaging techniques
Optoelectronic Displays
Laser projection (speckle reduction)
AR/VR near-eye displays (eyebox expansion)
Integral imaging (true 3D displays)
Laser Engineering
Beam homogenization (diode laser coupling)
Multi-focus parallel processing
Free-space optical communications
Emerging Fields
Quantum optics (single-photon detection)
Biochips (high-throughput screening)
ToF sensor optimization
IV. Fabrication Methods
Photoresist reflow process
Gray-scale lithography
Nanoimprint lithography
Laser direct writing
V. Development Trends
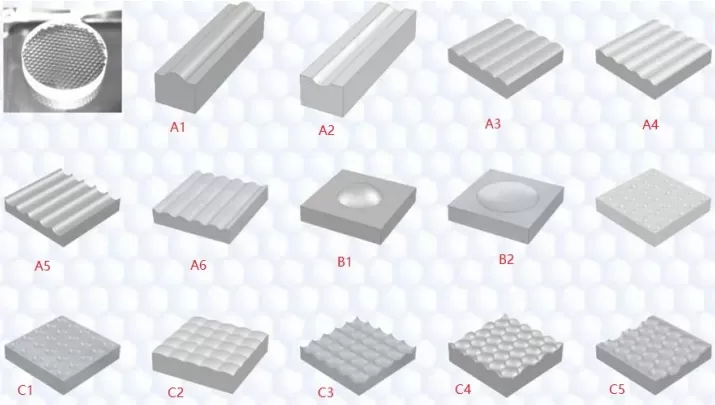
Freeform array configurations
Multi-level hybrid structures
Tunable MLAs (MEMS/liquid crystal)
Metalens-based MLAs (subwavelength features)


















 EN
EN